 Highest Rates of Obesity, Diabetes in the South, Appalachia,
Highest Rates of Obesity, Diabetes in the South, Appalachia,
and Some Tribal Lands
Estimates of Obesity Now Available for all U.S. Counties
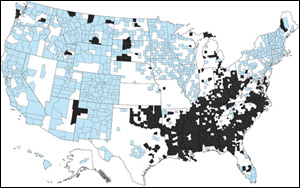 | |
Wide sections of the Southeast, Appalachia, and some tribal lands in the West and Northern Plains have the nation's highest rates of obesity and diabetes, according to estimates released today by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. In many counties in those regions, rates of diagnosed diabetes exceed 10 percent and obesity prevalence is more than 30 percent.
The estimates, in this week's Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, are the first to provide county-level snapshots of obesity across the United States. They also update diabetes county-level estimates released in 2008. To view the County-level estimates of obesity and diagnosed diabetes visit Diabetes Data and Trends .
Eighty-one percent of counties in the Appalachian region that includes Kentucky, Tennessee, and West Virginia have high rates of diabetes and obesity. So do three-quarters of counties in the southern region that includes Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, and South Carolina.
"Diabetes is costly in human and economic terms, and it's urgent that we take action to prevent and control this serious disease," said Dr. Ann Albright , director of CDC's Division of Diabetes Translation . "The study shows strong regional patterns of diabetes and can help focus prevention efforts where they are most needed."
The proportion of U.S. adults who are obese was 26.1 percent in 2008, according to Behavior Risk Factor Surveillance System, (BRFSS) data. CDC estimates that nearly 8 percent of the population, or about 24 million people, have diabetes. Of these, 5.7 million are undiagnosed.
"The small-area estimates for obesity will be an important tool to help communities better understand and battle this serious public health problem. Communities are in the best position to prevent and reduce obesity among their citizens through innovative programs," said Dr. William H. Dietz , director of CDC's Division of Nutrition, Physical Activity and Obesity .
The medical costs of obesity reached an estimated $147 billion in 2008, and the medical costs of diabetes were $116 billion. People with diagnosed diabetes have medical costs that are 2.3 times higher than those without the disease.
 | |
Obesity is one of several factors linked to type 2 diabetes. Where people live, how much money they earn, their culture and their family history also play a role. An unhealthy diet, lack of physical activity, and socioeconomic factors contribute to both obesity and type 2 diabetes as well as to complications of diabetes. Some population groups also are at higher risk, including a number of racial and ethnic minorities.
CDC and its partners are working on a variety of initiatives to prevent type 2 diabetes and to reduce obesity. CDC has recommended 24 community strategies to prevent obesity , from providing greater access to healthy foods to redesigning communities to encourage more physical activity. The agency is also in a new partnership with state, federal, and nonprofit agencies targeting health disparities in Mississippi, which has the nation's highest obesity rate and one of the highest rates of diabetes. CDC's national diabetes prevention and control program provides resources and technical assistance to state health departments, national organizations, and communities.
For More Information
- Estimated County-Level Prevalence of Diabetes and Obesity - United States, 2007
MMWR, November 20, 2009 / 58(45);1259-1263
Also available in a PDF version . (PDF-2.5Mb) - Diabetes Data and Trends
County-level estimates of obesity and diagnosed diabetes. - Obesity and Overweight
CDC′s efforts in the fight against obesity. - Diabetes Public Health Resources
Information on diabetes and preventing the disease. - National Diabetes Education Program (NDEP)
Develops and disseminates educational information on the prevention and control of diabetes and offers a wide range of resources. - Healthy Weight
It's not a diet, it's a lifestyle! - We Can Be Stronger than Diabetes
Listen to this series and other podcasts on diabetes.
